Problems Addressed
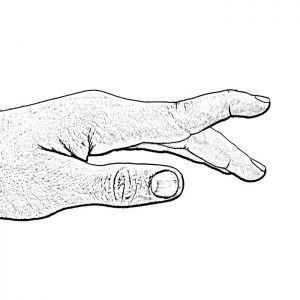
Hyperextension
Hyperextension of a finger joint beyond the neutral position may result in a painful joint, decreased power when pinching and a delay in being able to bend the finger.
View Splinting Solutions >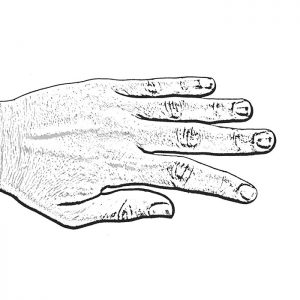
Lateral Instability
Sideways deviation of a finger may result in a painful joint, disrupted normal movement, and an unstable finger, which crosses under an adjacent one. It is accentuated when force is applied during pinching or lifting.
View Splinting Solutions >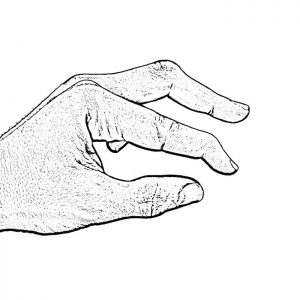
Flexion
Flexion is the inability to actively straighten a finger joint to its neutral position which may result in a painful joint or the inability to open the hand wide enough to grasp objects.
View Splinting Solutions >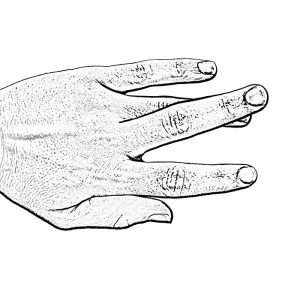
MP Deviation
MCP Problems include instability of the joints at the base of the finger (the knuckle joints) which allow the fingers to stray to the side or cross over or under each other, making it difficult to hold objects or work on a computer.
View Splinting Solutions >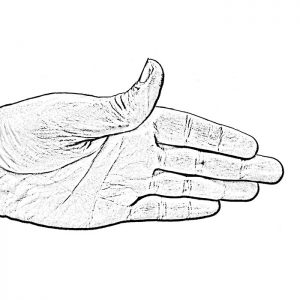
Thumb IP Problems
Thumb IP Problems include hyperextension of the end of the thumb beyond the neutral position which may result in a painful joint, decreased power when pinching and difficulty picking up or manipulating small objects.
View Splinting Solutions >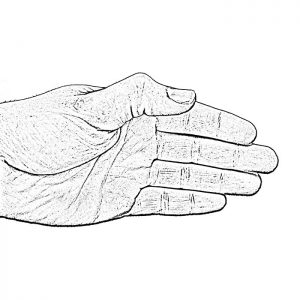
Thumb MCP Problems
Thumb MCP Problems include hyperextension of the end of the thumb beyond the neutral position may result in a painful joint, decreased power when pinching and difficulty picking up or manipulating small objects.
View Splinting Solutions >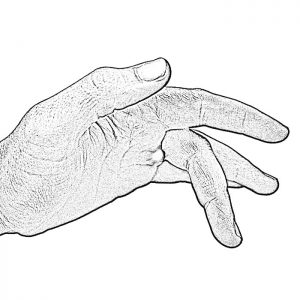
Triggering
Triggering occurs when a nodule or inflammation and “thickening” on the flexor tendon causes irregular movement of the finger. The finger feels “locked” in the bent position.
View Splinting Solutions >
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes are a group of connective tissue disorders. One of the most common symptoms is joint hypermobility which causes loose/unstable joints, pain, dislocations and early onset of osteoarthritis.
View Splinting Solutions >